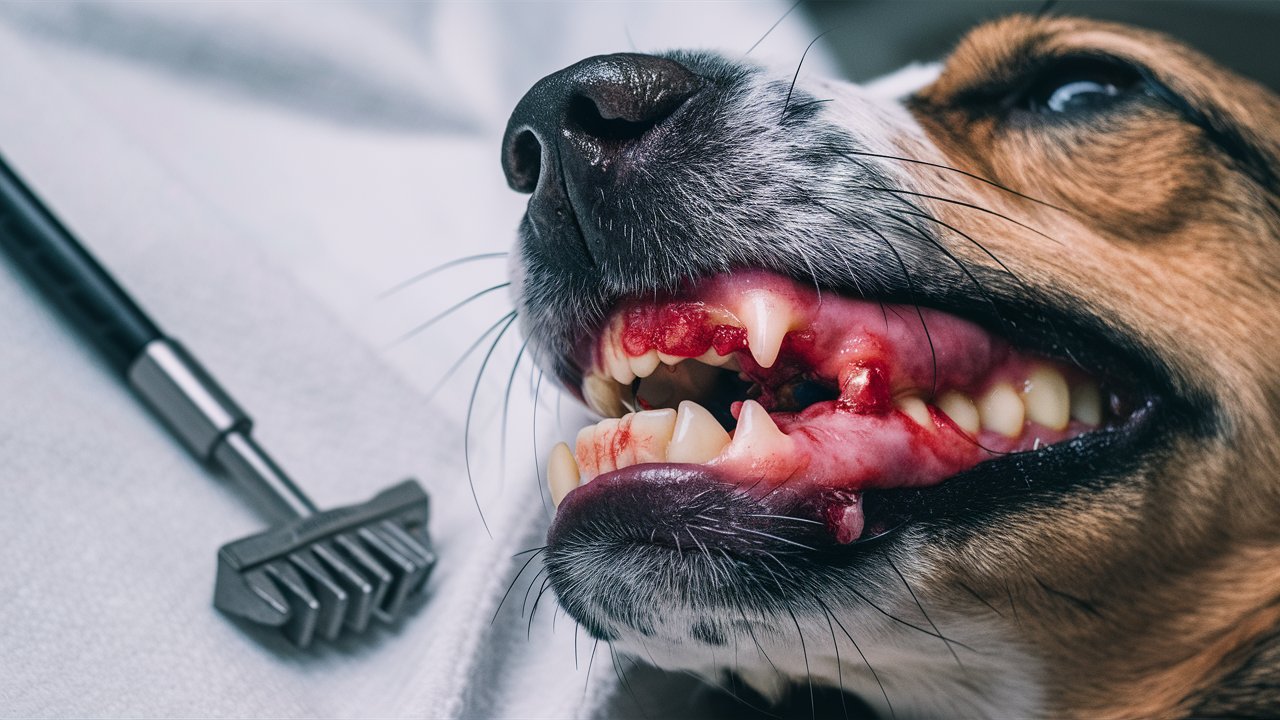

Gingivitis and Dental Care in Dogs
Caring for your dog’s dental health is more critical than many pet owners realize. Gingivitis, an inflammation of the gums, is a common condition affecting dogs of all ages and breeds. Left unchecked, it can lead to more severe dental issues and impact your pet’s overall well-being. This blog post will explore the signs, causes, and preventive measures of gingivitis, offering valuable insights to ensure your furry friend’s mouth stays healthy and pain-free. Understanding the importance of dental care can significantly impact your dog’s quality of life.
Understanding Gingivitis in Dogs
Gingivitis, an inflammation of the gums, is a prevalent dental issue in dogs. It’s the early stage of periodontal disease and, if untreated, can progress to more severe conditions. Understanding gingivitis can help you better care for your dog’s dental health and prevent further complications.
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums caused by bacteria in the mouth. When food particles and saliva mix, they form plaque, which hardens into tartar if not removed. This tartar harbours bacteria that irritate the gums, causing redness and swelling. Dogs with gingivitis may exhibit various symptoms that signify the onset of this condition.
Causes of Gingivitis in Dogs
Several factors contribute to the development of gingivitis in dogs, and recognizing these can help in prevention:
- Plaque Buildup: The primary cause is the buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. This can happen when a dog’s teeth are not cleaned regularly.
- Poor Diet: A diet lacking proper nutrients can weaken your dog’s immune system, making it tougher for the body to fight gum infections.
- Lack of Dental Care: Infrequent brushing of your dog’s teeth and irregular dental check-ups can lead to plaque accumulation.
- Crowded Teeth: Dogs with crowded or misaligned teeth are more prone to food and plaque getting trapped, leading to gingivitis.
- Age: Older dogs are more susceptible to dental problems, including gingivitis.
Symptoms of Gingivitis in Dogs
Identifying gingivitis early can prevent more severe dental issues. Keep an eye out for the following symptoms in your dog:
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath can be one of the first indicators of gingivitis.
- Red or Swollen Gums: Healthy gums are pink, so any redness or swelling is a sign of inflammation.
- Difficulty Eating: Dogs with gingivitis might find it painful to chew, leading to a reduced appetite or favouring one side of the mouth.
- Bleeding Gums: You might notice bleeding, especially when your dog is eating or when you brush their teeth.
- Pawing at the Mouth: If your dog frequently paws at their mouth, it could be due to discomfort from inflamed gums.
- Drooling: Excessive drooling can also indicate oral discomfort or pain.
Understanding these symptoms and their causes can help you take the necessary steps to address gingivitis early. Regular dental care and check-ups are essential in maintaining your dog’s oral health and overall well-being.
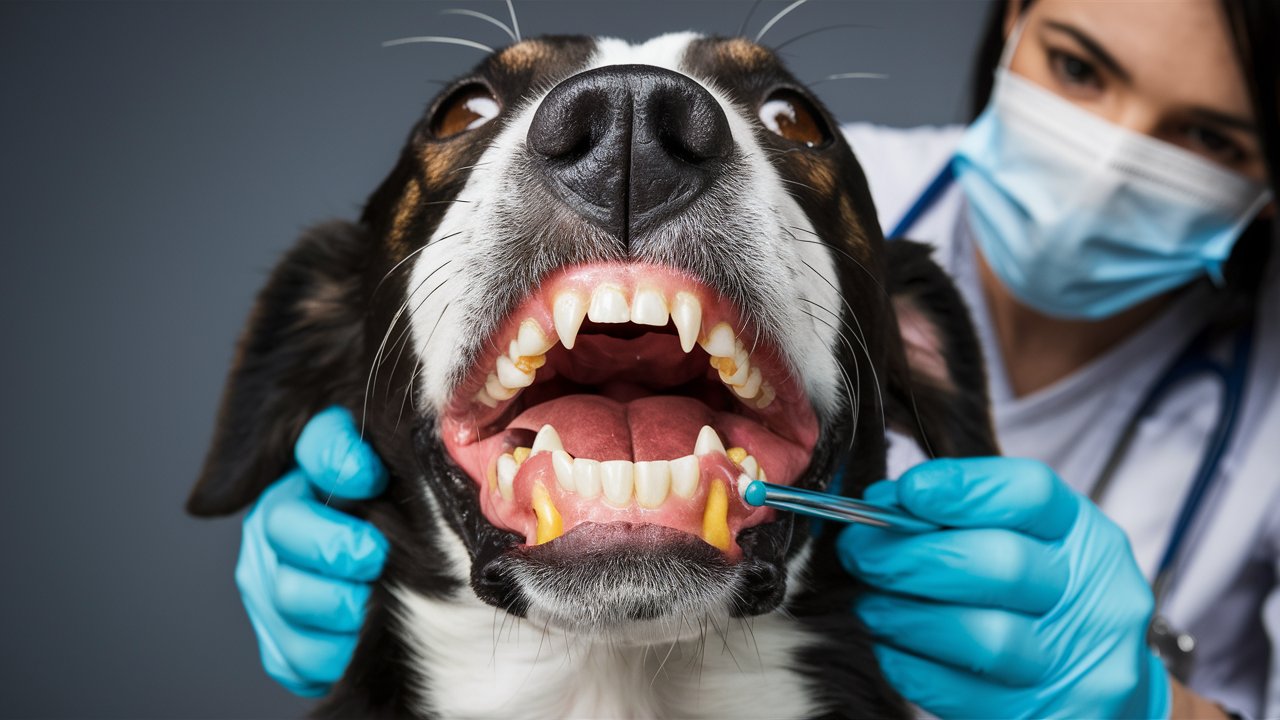
Importance of Dental Care for Dogs
Proper dental care is vital for your dog’s health. Just like in humans, dental issues in dogs can lead to severe health problems if neglected. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene can prevent many of these issues, ensuring your furry friend stays happy and healthy.
Preventing Systemic Health Issues
Untreated dental problems can have serious consequences beyond the mouth. When bacteria from dental diseases like gingivitis enter the bloodstream, they can affect vital organs, leading to severe health conditions.
Heart Disease: Bacteria from the mouth can travel to the heart, causing infections in the heart valves and lining, known as endocarditis. This can lead to heart failure if not addressed promptly.
Kidney Disease: Bacteria reaching the kidneys can cause infections and inflammation, leading to chronic kidney disease. This can significantly impact your dog’s overall health and quality of life.
When neglecting your dog’s dental health, you risk more than bad breath. Regular dental care helps in keeping these serious ailments at bay.
Maintaining Quality of Life
Good dental care significantly enhances your dog’s quality of life. Just like humans, dogs experience discomfort and pain due to dental issues. By maintaining their dental health, you can ensure they live more comfortably.
Reducing Pain and Discomfort: Dogs with dental problems often experience pain while eating, leading to decreased appetite and possible malnutrition. Regular brushing and dental check-ups can prevent this discomfort.
Preventing Tooth Loss: Neglected dental issues can lead to tooth loss, making it difficult for your dog to chew food properly. Proper dental care maintains their teeth in good condition, allowing them to enjoy their meals fully.
Enhanced Playtime: Dental issues can make playtime painful for dogs, especially those who love to chew toys. Healthy teeth ensure they can play without pain, keeping them active and happy.
Proper dental care is essential for preventing severe health issues that can affect your dog’s organs and maintaining their quality of life by reducing pain and discomfort. Regular check-ups and at-home dental care routines are crucial in ensuring your beloved pet stays healthy and happy.
Effective Dental Care Practices
Keeping your dog’s teeth clean isn’t just about fresh breath; it’s crucial for their health. Regular dental care can prevent serious health problems and improve your dog’s quality of life.
Regular Brushing
Brushing your dog’s teeth is one of the most effective ways to maintain their dental health. Here’s how you can do it properly:
- Use the Right Tools: Get a toothbrush designed for dogs. These usually have softer bristles and are angled to reach the back teeth. Choose a dog-specific toothpaste, as human toothpaste can be harmful to dogs.
- Get Your Dog Comfortable: Start by letting your dog get used to the taste of the toothpaste. Put a small amount on your finger and let them lick it off. Gradually introduce the toothbrush.
- Proper Technique: Hold the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to the teeth. Use gentle, circular motions, focusing on the gumline where plaque tends to accumulate. Brush the outer surfaces of the teeth; the tongue naturally cleans the inner surfaces.
- Frequency: Aim to brush your dog’s teeth at least two to three times a week. Daily brushing is ideal but can be challenging for some pet owners.
Professional Dental Cleaning
Regular veterinary dental cleanings are crucial in maintaining your dog’s oral health. Here’s what you need to know:
- Importance: Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that brushing at home can’t reach. This helps to prevent gingivitis and other dental diseases.
- What to Expect: During a professional dental cleaning, your veterinarian will likely use anaesthesia to keep your dog calm and still. They will then thoroughly clean, including scaling (removing tartar) and polishing the teeth.
- Frequency: The frequency of professional cleanings depends on your dog’s age, breed, and dental health. Generally, most dogs benefit from a professional cleaning once a year, but some may need them more frequently.
Dental Chews and Toys
Dental chews and toys can be a fun and effective way to help keep your dog’s teeth clean. Here are some benefits:
- Fight Plaque: Many dental chews are designed to help scrape off plaque and tartar as your dog chews on them.
- Promote Healthy Gums: Chewing helps stimulate the gums, increasing blood flow and promoting overall gum health.
- Entertaining and Engaging: Chewing is a natural behaviour for dogs, and providing them with dental chews or toys can keep them occupied and prevent destructive chewing behaviours.
Tips for Choosing Dental Products:
- Look for products with the Veterinary Oral Health Council (VOHC) seal, indicating they meet specific standards for plaque and tartar control.
- Opt for chews that are appropriately sized for your dog to prevent choking hazards.
Diet and Nutrition
Your dog’s diet plays a significant role in their dental health. Here’s how you can ensure their diet supports healthy teeth and gums:
- Kibble vs. Wet Food: Dry kibble can be better for dental health as it helps scrape off plaque while your dog chews. However, some dogs may require wet food for medical reasons.
- Special Dental Diets: Some dog foods are formulated to improve dental health. These diets often include bigger kibble designed to reduce plaque and tartar.
- Healthy Snacks: Avoid giving your dog sugary or starchy treats that can contribute to plaque buildup. Instead, choose healthy options like carrots, apple slices (without seeds), and specially formulated dental treats.
- Balanced Nutrition: Ensure your dog gets a balanced diet that meets all their nutritional needs. This helps strengthen their immune system, making fighting off infections, including gum disease, easier.
Incorporating these effective dental care practices into your routine can help ensure your dog’s teeth stay healthy and strong. Regular brushing, professional cleanings, dental chews, and a balanced diet are crucial in maintaining your dog’s oral health.
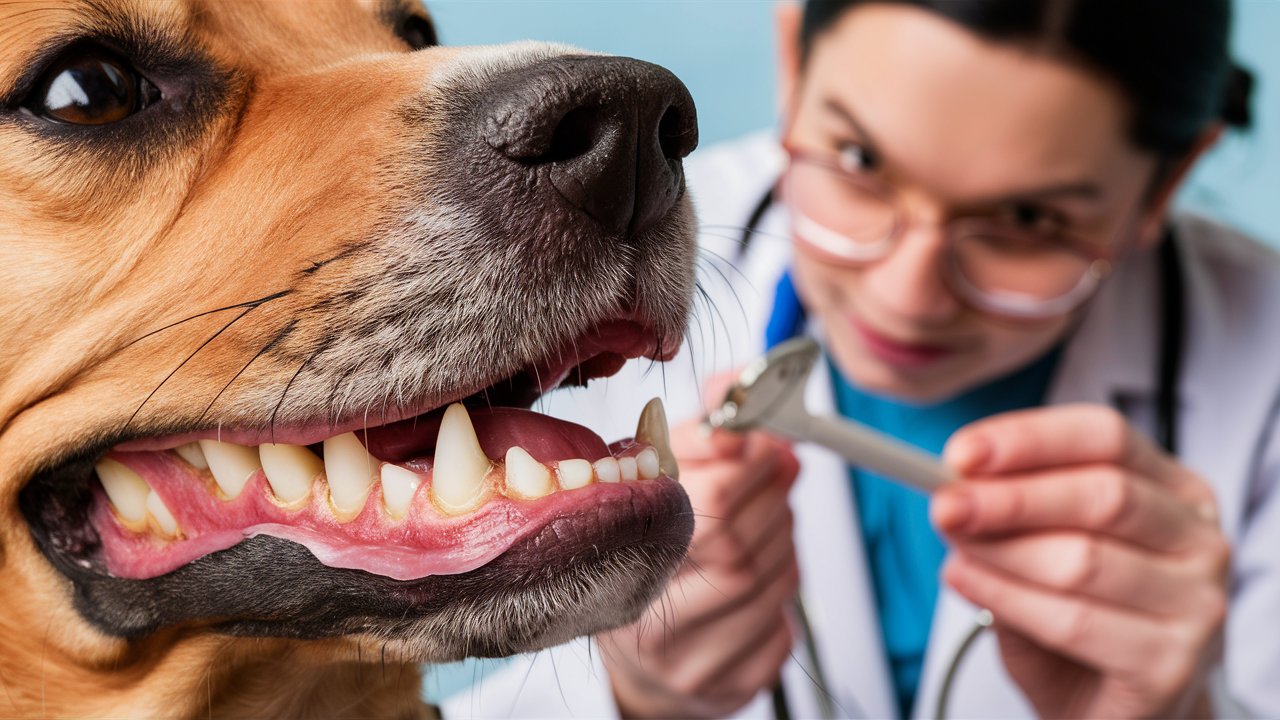

Recognizing and Treating Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common dental issue in dogs, but recognizing it early and getting proper treatment can significantly affect your pet’s health. Here’s how to spot the early signs of gingivitis and what steps to take for treatment.
Early Detection
Detecting gingivitis early can prevent serious dental problems. Here are some tips to help you catch the signs at home:
- Monitor Bad Breath: Although it’s common for dogs to have slightly bad breath, a sudden and persistent foul smell may indicate gingivitis.
- Inspect Gums: Healthy gums should be pink. Red, swollen, or bleeding gums are signs of inflammation.
- Watch Eating Habits: If your dog is avoiding food, chewing on one side, or dropping food, it could be due to gum pain.
- Look for Behavior Changes: Pawing at the mouth, excessive drooling or reluctance to play with toys can be signs of oral discomfort.
- Regular Home Checks: Lift your dog’s lips and gently inspect their mouth weekly. Look for tartar buildup and changes in gum colour or texture.
Early detection of gingivitis can help avoid more severe dental issues requiring extensive treatment.
Veterinary Treatments
A visit to the vet is crucial if you suspect your dog has gingivitis. Vets use several treatments to address the issue:
- Professional Cleaning: Under anaesthesia, your vet thoroughly cleans your dog’s teeth, removing plaque and tartar above and below the gum line. This process is known as scaling.
- Medications: Antibiotics or antiseptic gels may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and combat bacterial infections.
- Pain Management: If your dog is in pain, your vet may recommend pain relief options to make it more comfortable during the healing process.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular check-ups are essential to monitor your dog’s progress and ensure that gingivitis does not return.
Your veterinarian may also offer advice on improving your dog’s oral hygiene routine at home to prevent future issues.
Home Remedies and Care
While professional help is essential, you can also take steps at home to support your dog’s dental health:
- Brushing Their Teeth: Use dog-specific toothbrushes and toothpaste. Aim to brush their teeth at least two to three times a week.
- Dental Chews: Provide dental chews designed to reduce plaque and tartar buildup. Look for products with the Veterinary Oral Health Council (VOHC) seal of approval.
- Oral Rinses: Use dog-safe oral rinses to help control plaque and bacterial growth.
- Healthy Diet: Feed your dog a balanced diet that promotes healthy teeth and gums. Some pet foods are specifically formulated for dental health.
- Regular Inspections: Check your dog’s mouth regularly for signs of gingivitis and other dental issues.
Home care routines combined with professional treatments can keep gingivitis at bay and ensure your dog enjoys a healthy mouth and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Maintaining your dog’s dental health is essential to preventing gingivitis and ensuring their overall well-being. Regular brushing, professional cleanings, and a balanced diet are key practices to keep their teeth and gums healthy. Early detection of gingivitis through routine checks can prevent progression to more severe conditions. By prioritizing dental care, you’re protecting your dog’s oral health and supporting their longevity and quality of life. Consistent dental care is critical to responsible pet ownership and contributes significantly to your dog’s happiness and comfort.
